JVM (Java Virtual Machine) Architecture
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is an abstract machine. It is a specification that provides runtime environment in which java bytecode can be executed.
JVMs are available for many hardware and software platforms (i.e. JVM is platform dependent).
What is JVM?
Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is a engine that provides runtime environment to drive the Java Code or applications. It converts Java bytecode into machines language.
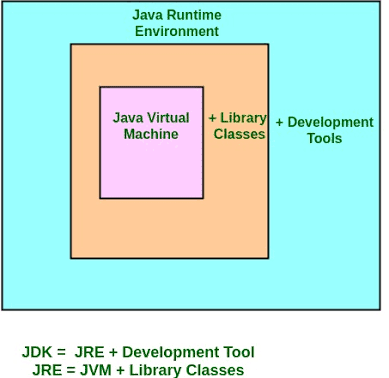
JVM is a part of Java Run Environment (JRE). In other programming languages, the compiler produces machine code for a particular system. However, Java compiler produces code for a Virtual Machine known as Java Virtual Machine.
How JVM works?
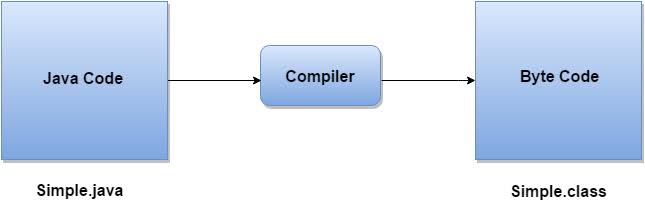
First, Java code is complied into bytecode. This bytecode gets interpreted on different machines
Between host system and Java source, Bytecode is an intermediary language.
JVM is responsible for allocating memory space.
JVM Architecture
Let's understand the Architecture of JVM. It contains classloader, memory area, execution engine etc.
1) ClassLoader
The class loader is a subsystem used for loading class files. It performs three major functions viz. Loading, Linking, and Initialization.
2) Method Area
JVM Method Area stores class structures like metadata, the constant runtime pool, and the code for methods.
3) Heap
All the Objects, their related instance variables, and arrays are stored in the heap. This memory is common and shared across multiple threads.
4) JVM language Stacks
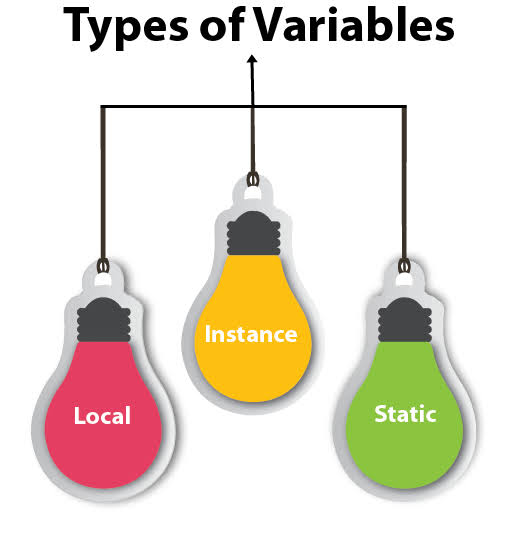
Java language Stacks store local variables, and it’s partial results. Each thread has its own JVM stack, created simultaneously as the thread is created. A new frame is created whenever a method is invoked, and it is deleted when method invocation process is complete.
5) PC Registers
PC register store the address of the Java virtual machine instruction which is currently executing. In Java, each thread has its separate PC register.
6) Native Method Stacks
Native method stacks hold the instruction of native code depends on the native library. It is written in another language instead of Java.
7) Execution Engine
It is a type of software used to test hardware, software, or complete systems. The test execution engine never carries any information about the tested product.
8) Native Method interface
The Native Method Interface is a programming framework. It allows Java code which is running in a JVM to call by libraries and native applications.
9) Native Method Libraries
Native Libraries is a collection of the Native Libraries(C, C++) which are needed by the Execution Engine.







0 Comments